Liners are protective membranes used in various applications to prevent leakage, contain liquids, and protect underlying surfaces. They are commonly made from materials such as polyethylene, polypropylene are utilized across industries including agriculture, construction, waste management, and environmental protection.

Types of Liners
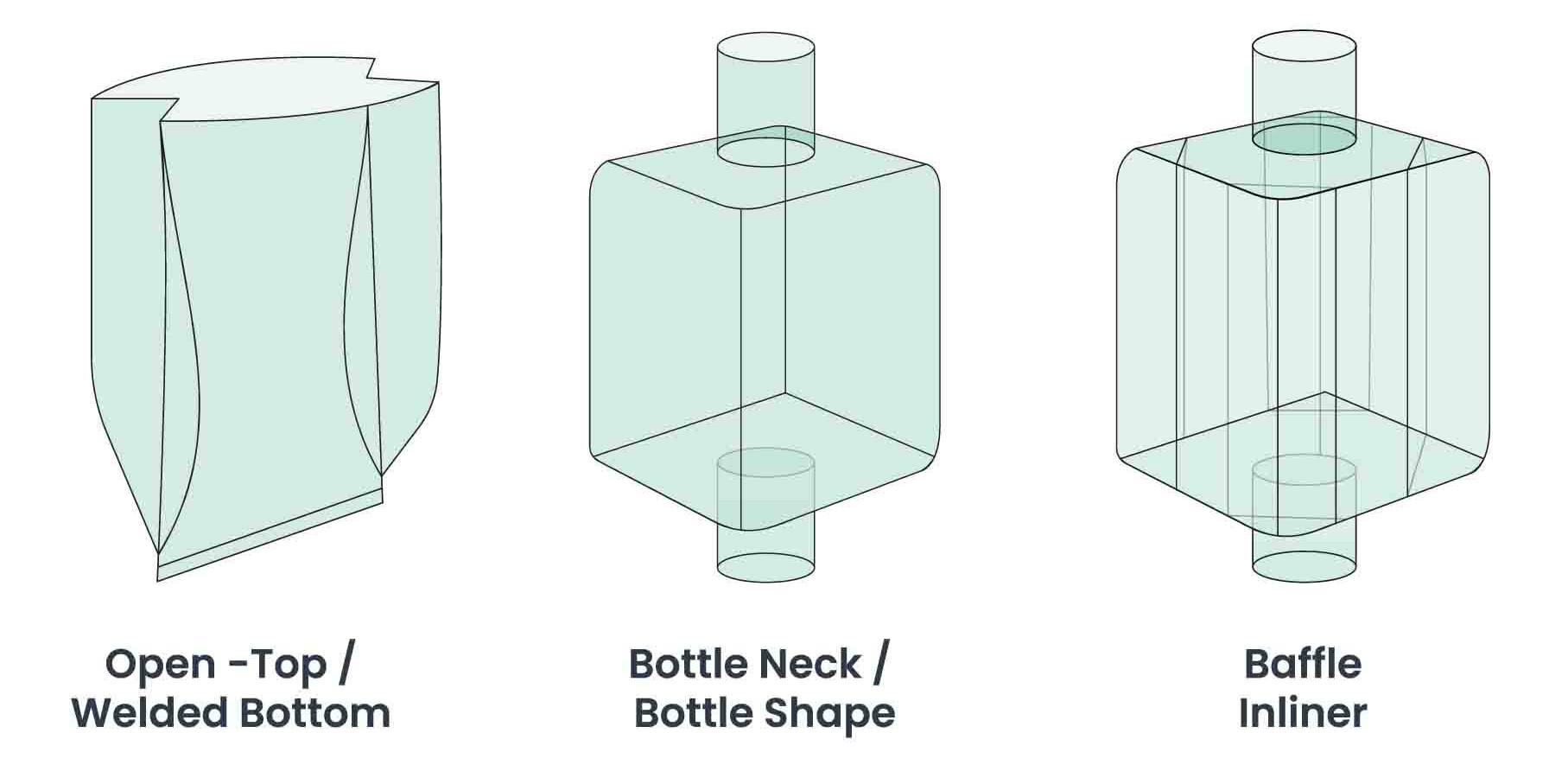
Linear Inline big bag
Applications of Liners
Key Features of Liners
-
Enhanced Protection :
Provides an additional barrier against moisture, air, water vapor, and light exposure, ensuring product integrity. -
Product Safety :
Protects sensitive materials from contamination and environmental factors. -
Versatility :
Suitable for a wide range of applications, including food, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and construction materials. -
Customizable Options :
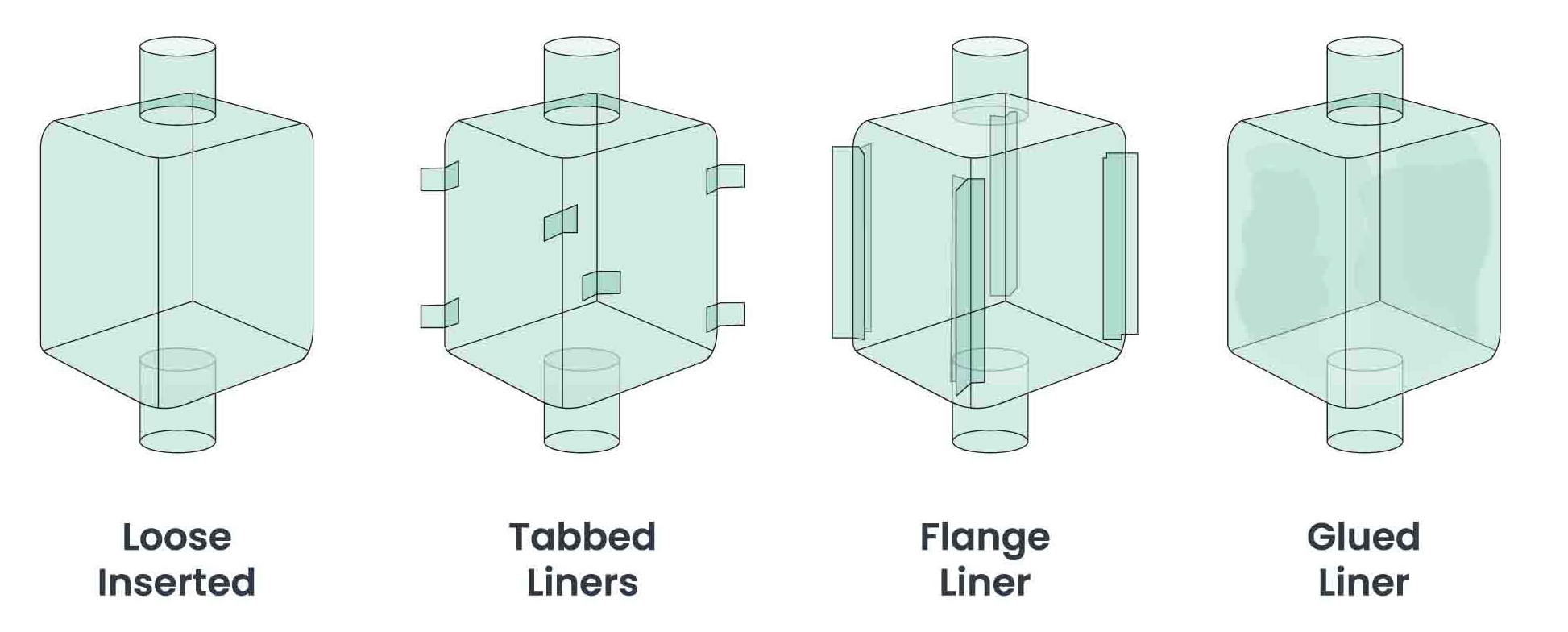
Available in various types (Loose, Glued, Tabbed, Stitched) and materials (LDPE, LLDPE & HDPE). -
Improved Material Retention :
Reduces the risk of leakage for fine powders, liquids, and granular products. -
Static Control :
Conductive and antistatic liners minimize risks in static-sensitive or flammable environments. -
Maintained Shape and Stability :
Baffle liners help the bag retain its form during filling and transportation. -
Cost-Effective Solution :
Reduces product loss and ensures safe transportation, minimizing operational costs. -
Compliance and Safety :
Meets industry standards for hygiene, especially in food-grade and pharmaceutical applications.